80-82 Cao Duc Lan, District 2, HCMC, Vietnam
+84 76 865 6688
info@beetech.com.vn
+84 76 865 6688
About us
Contact us
80-82 Cao Duc Lan, District 2, HCMC, Vietnam
+84 76 865 6688
info@beetech.com.vn
+84 76 865 6688
About us
Contact us

What is RFID? A Comprehensive Guide to RFID Technology and Its Prominent Applications in Daily Life
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is an automation technology that allows information about an object to be collected and transmitted remotely via radio waves. This technology has become an essential part of many fields, especially in inventory management and supply chain logistics. With its ability to identify quickly and accurately, RFID not only helps businesses optimize workflows but also enhances the tracking and control of goods in real-time. In this article, we will explore RFID technology in depth, how it works, its benefits in warehouse management, applications in logistics and supply chains, and the challenges businesses face when implementing RFID systems.
To better understand RFID, we need to grasp the basic concept and the history of the development of this technology.
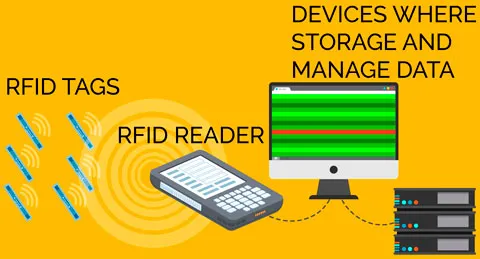
RFID is a technology that allows for the automatic identification of an object without direct contact. An RFID system consists of three main components: RFID tags, RFID readers, and management software. RFID tags contain encoded information and can be attached to products, packages, or even people. The RFID reader is responsible for scanning and collecting information from the RFID tags within a certain range.
Initial Ideas: The principles of radio waves and magnetic fields were demonstrated by James Clerk Maxwell (1864) and Heinrich Hertz, laying the groundwork for RFID technology.
Nikola Tesla: A pioneer in developing wireless communication systems.
Radar and IFF (Identify Friend or Foe): The British military developed the IFF system to identify allied aircraft by sending signals to planes; if the aircraft responded, it was identified as “friend.” This is considered the precursor to modern RFID technology.
RFID began commercialization and was used in fields such as:
However, RFID systems were still quite expensive and used only in specific fields.
Auto-ID Center at MIT (1999): A significant turning point. The Auto-ID Center researched RFID and developed the EPC (Electronic Product Code) standard for product identification.
Major corporations like Procter & Gamble, Gillette, Walmart, and Coca-Cola began exploring and testing RFID for product tracking in supply chains.
Combining AI + IoT + Blockchain: Enhancing traceability and real-time data analysis capabilities.
Battery-free or ultra-small RFID: Serving the healthcare, logistics, and smart consumer goods sectors.
In addition to logistics and supply chain applications, RFID is used in various fields such as:
To understand RFID technology better, we need to explore how this system operates.
An RFID system typically consists of three main components: RFID tags, RFID readers, and management software. Each component plays a crucial role in collecting and processing information.
When an RFID tag enters the scanning area of a reader, the reader emits radio waves. The tag receives this signal and responds by transmitting the encoded information contained within it. This allows the reader to quickly and efficiently record the information.
The interaction between the RFID tag, reader, and software occurs continuously and rapidly. When an item is tagged and moves through the scanning area, the system automatically updates information about the item’s location and status, creating a comprehensive tracking system.
RFID technology offers numerous benefits for warehouse management, helping businesses optimize processes and reduce costs.
Companies like Amazon, Zara, Decathlon, and Walmart have implemented RFID to manage millions of products daily, speeding up order processing and optimizing inventory.
RFID has proven its strength in improving logistics and supply chain processes. Here are some notable applications of this technology.
In the current RFID market, there are many different devices catering to diverse needs. Here are some popular devices:
The main components of an RFID system. They come in various shapes and sizes, from small tags attached to products to larger tags used for pallets or packages. Each type of tag has its advantages, depending on the intended use.

Devices used to scan and collect information from RFID tags. They can be equipped with different technologies suitable for various working environments. Some readers allow connection to other management systems, enhancing tracking and data analysis capabilities.

Typically installed near readers, antennas are responsible for transmitting and receiving radio waves from RFID tags. The design of the antenna significantly affects the scanning range and accuracy of information collection.

Management Software:
An essential element of an RFID system. It organizes and analyzes data collected from readers, helping businesses make accurate and timely decisions.
Although RFID offers many benefits, implementing this technology also presents several challenges.
High Initial Investment Costs:
One of the biggest challenges in implementing RFID is the relatively high initial investment. Not only do businesses need to purchase equipment, but they also need to build management software systems and train employees. This can pose difficulties for many companies, especially small businesses.
Compatibility Issues:
RFID technology may not be compatible with existing systems within the company. Integrating RFID into workflows requires time and effort, which can disrupt business operations.
Employee Training:
Implementing new technology always requires employees to be trained to use the system effectively. This not only takes time but also requires commitment from management to ensure that employees have the necessary skills and knowledge.
Both RFID and barcodes are automatic identification technologies, but they have distinct differences.
RFID technology faces both challenges and opportunities in the future. The development of new technologies, such as IoT, promises to open up new possibilities for RFID.
The combination of RFID and the Internet of Things (IoT) will create significant breakthroughs in supply chain management. With IoT connectivity, information from RFID can be shared and analyzed instantly, providing a comprehensive view of logistics processes.
Innovations in technology will enhance the performance of RFID, increasing accuracy and device coverage. This will help mitigate cost and performance issues in implementing the technology.
As security issues are a major challenge when using RFID, developing new security solutions is essential. This will give businesses more confidence in using this technology.
Finally, enhancing awareness and understanding of RFID technology is crucial. Businesses need education and training about the benefits of RFID to fully leverage this technology in warehouse management and supply chains.
With over 12 years of experience in the AutoID field (including barcodes, RFID, etc.), Beetech proudly stands as a leading provider of intelligent solutions and equipment in Vietnam.
The combination of a highly experienced expert team and a commitment to delivering quality solutions at optimal costs has made Beetech a trusted partner for many businesses both domestically and internationally.
With a mission to develop information technology, particularly in the Auto ID field (RFID, Barcode, AI), Beetech remains steadfast on its chosen path, continuously researching and improving to provide customers with quality products and services.
Contact Us:
📧 Email: info@beetech.com.vn
🌐 Website: https://beetech.com.vn



RFID in Logistics – The Core Technology Powering Modern Supply Chains
17/11/2025 06:21:25

RFID – The “Silent” Technology Transforming How Vietnamese Businesses Manage Their Inventory
13/11/2025 07:16:17

National Assembly Proposes Using Electronic Chips to Monitor Drug Addicts
12/11/2025 03:56:38

Vietnam’s RFID Logistics Market: Rapid Growth from 2025 to 2031
12/11/2025 03:13:47

RFID – When data becomes reality: The journey to building systems of reality in the digital ge
07/11/2025 02:57:55

Challenges in RFID Reading Performance and Environmental Conditions
06/11/2025 02:36:26